Catalyst
Introduction
Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required. Tungsten and molybdenum compounds used in catalysis has reached 60 years of history.
History
One day, the Swedish chemist Berzelius was busy in experiments in a chemistry lab. In the evening, his wife Maria prepare the food and wine banquet relatives and friends to congratulate her birthday. Berzelius immersed in the experiment, complete forgetfulness of it, until Maria pulled him out of the lab, he suddenly realized, in a hurry to get home. On entering the room, guests toast to congratulate him, he can not attend to wash their hands to take over a cup of peach wine in one gulp. When he filled a second glass of wine, but frowned and shouted: " Maria!, how can you let me drink vinegar," Mary and guests are shocked. Maria carefully looked at the bottle, and poured a cup to taste, it is completely the mellow peach wine! Berzelius gave her his cup, Maria drank and nearly all spit it out, said: "How can the sweet wine become vinegar?" Guests have come nearer, watching this strange "God Cup".
Berzelius discovered that there is a small amount of black powder in the glass. He glanced at his own hand, found that hands are covered coated with black platinum. Originally, the magic of the wine into acetic acid is derived from the platinum powder which acceleratesa chemical reaction of the ethanol (alcohol) and oxygen in the air, and them produce acetic acid. Later, it was called as catalytic, the Greek meaning is "solution to bondage."
Application
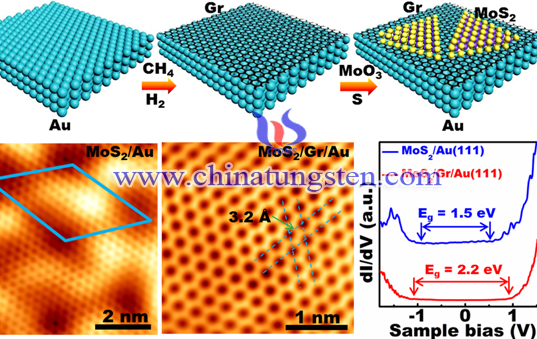
Catalysts are widely used in industry. Molybdenum disulfide is one of them. Before World War II, German scientists invented a molybdenum-based catalysts, which was used as liquefaction of coal. Mainly because of its high activity and good anti-poisoning ability, molybdenum disulfide can be used as a catalyst. At the same time, such catalysts also further enhance the reaction rate and selectivity optimizatio by adding Co and Ni.

