Molybdenum Disulfide Hexagonal Phase Nanoparticle
Manufacturing Process
The 0.412g (NH4) 2Mo2O7 · 4H2O and 1.92g Na2S · 9H2O is dissolved in 100mL deionized water, and 0.08mol hydrochloric acid is added to prepare (NH4) MoS4. After thirty minutes, the 100mL of aqueous solution containing 1gSDBS and 2mL hydrazine hydrate and appropriate amount of aqueous ammonia are added in it, pH is adjusted to 9-10. The mixture is then heated to 100℃ temperature and holding for two hours. MoS2 sample is placed in Ar, and calcined at a temperature of 400℃ for half an hour, thereby improving the degree of crystallization.
The surfactant can be constructed in a relatively isolated from the reaction solution domains, with the help of liquid phase reaction, the product would grow in according with its intrinsic structure and obtain the relatively regular morphology structure, and molybdenum disulfide belongs to the hexagonal system, therefore, hexagonal nanoparticles can can be prepared by liquid reduction.
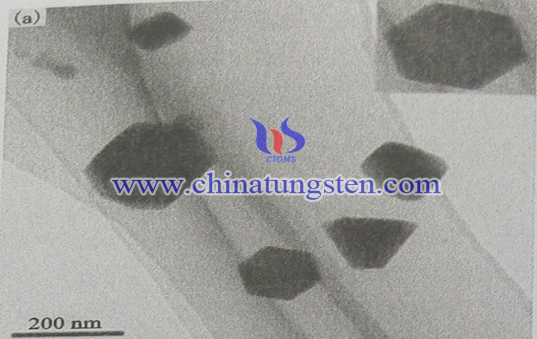
It can be seen from the TEM photograph molybdenum sulfide nano-particles in the figure, the diameter of the resulting product made by liquid phase reduction method is about 100 ~ 200nm. However, most of the particles have not perfect morphology with coarse projections and rough edges, it should be because of the poor degree of crystallization of the product, resulting in incomplete crystal growth. Molybdenum disulfide belongs to the hexagonal, so it can be seen that some nanoparticles exhibit a perfect hexagonal structure. However, if do not add SDBS as a modifier, MoS2 product would not have a regular shape, and they would bond together to form a large floc. It can be concluded that the surfactant SDBS can not only contribute to the formation of the hexagonal structure, but also promote the dispersion of nanoparticles.

