Molybdenum Disulfide Nanosphere
Introduction
As an important lubricant additive, morphology of molybdenum disulfide play a decisive role for friction performance. Thanks to a unique mechanism of rolling friction, molybdenum disulfide and spherical fullerene structure can significantly improve the tribological properties. However, because the preparation of fullerene structure is more complex, people prefer to use a more simple method to prepare spherical molybdenum disulfide.
Firstly, 0.85g (NH4) 2Mo2O7 and 3.06g Na2S · 9H2O are dissolved in 100 mL of water, and then 2. 88g PEG-20000 (polyethylene glycol, molecular weight 20,000) is added. After the polyethylene glycol are dissolved, excess of hydrochloric acid is added, and stirred at high speed, 10 minutes later, a brown precipitate is collected. And successively use aqueous ammonia, ethanol and distilled water to wash them. The precipitate is then placed in a vacuum oven at a temperature of 50℃, dried for 6 hours and then placed in a tube furnace under a hydrogen atmosphere at a temperature of 900℃ calcined for half an hour. After the tube furnace cooled to room temperature, collect black powder, the powder is molybdenum disulfide nanosphere.
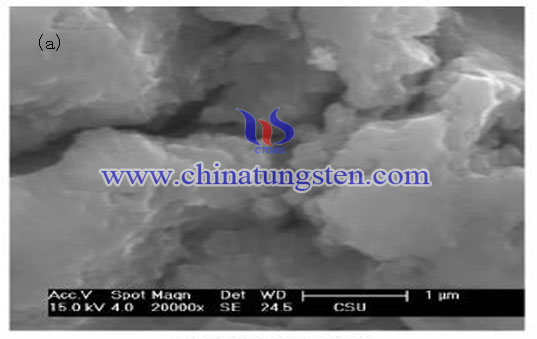
FIG.(a) and (b) shows the SEM image of the resulting sample molybdenum disulfide. When the coating agent PEG-20000 is not added, final product has serious agglomeration with the formation of large lumps. And after addition of PEG-20000, with the help of "steric hindrance", coating agents effectively dispersed nanocrystals of molybdenum disulfide, and through its own cover, prompting the formation of nanocrystals surfactants lowest energy structure of spherical, average size is about 100 nm, as shown in Figure (b).

