Molybdenum Disulfide Hollow Microsphere
Introduction
Due to special geometry and physical and chemical properties of hollow microspheres, it attaches much concern in the field of scientific research in recent years, these materials have a lot of interior space and nanoscale thickness of shell width, so that they are widely used in chemical, biological and photovoltaic field.
Manufacturing Process
2gPEG-20000 is added in 100mL of deionized water (C PEG = 1.0mmol·L-1), the temperature is raised to 90℃, stirring continuously until it is completely dissolved and then add 0.85g (NH4) 2Mo2O7 and 3.02g NaS2 · 9H2O. After thirty minutes, use hydrochloric acid to adjust pH to be neutral. Then add 0.75g NH2OH · HCl, and continue stirring for some time, if the color does not change then filtered and collect the dark brown precipitate. The product is washed with deionized water until neutral, and then washed with anhydrous ethanol three times, after high-speed centrifugation, dry it to air.
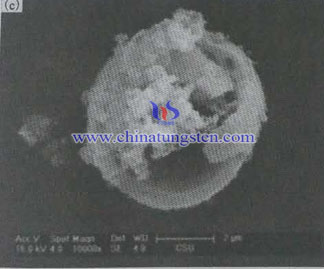
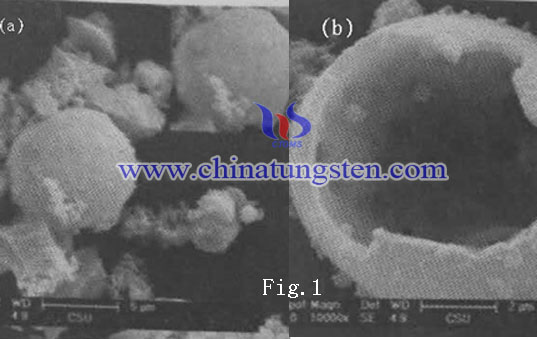
Pictures are SEM photograph of molybdenum disulfide hollow microspheres, whose morphology are the diameter of 2 ~ 7μm the spherical material, and accompanied by some broken hollow spherical shells due to a large external force. Surrounding of them are deposited with irregular molybdenum sulfide nanocrystals. Figure (b) shows morphology of molybdenum disulfide due to external force, it is clear that molybdenum disulfide is a hollow construction, constituted by the nanocrystalline with wall thickness of 0.2μm. Generally, because the bulb has an arcuate configuration which is relatively stable, the smaller the particle size, the more stable the sphere.