Molybdenum Disulfide Hollow Nanosphere
Introduction
Hollow nanospheres is a new nanostructure that has one obvious feature of great internal space and the thickness of nanoscale range of the shell.
Manufacturing Process
0.1gCTAC is added in 100mL of deionized water, the temperature is raised to 90℃, and then 0.85g (NH4) 2Mo2O7 and 3.06g NaS2 · 9H2O are added. After hoding for 30min, pH is adjusted to neutral by hydrochloric acid. After 30 minutes, add 0.75g NH2OH · HCl, and stirring constantly for some time, if the color does not change, obtain the final product. The product is washed with deionized water and after centrifugation, washed with anhydrous ethanol for several times, once after high-speed centrifugation, dry it to air.
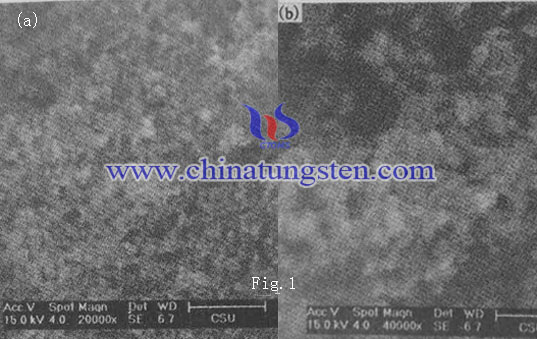
If the small particle size of the nanosphere shell structure is used in the field of catalysis, a high specific surface area of the structure will bring a lot of extra activity center, which will help enhance the overall catalytic performance. Figure 1 is a molybdenum disulfide hollow nanospheres of different magnification SEM image. It can be seen that the shape of the product is spherality, the particle size is small but unevenly distributed, mutual bond, there is a larger gap between the particles, which is porous structure (a). It can be found in FIG 1 (b)that MoS2 hollow nanosphere particle size is about 30 ~ 200nm, some of them are peanut-shell-like, but the particle size is too small to distinguish clean.
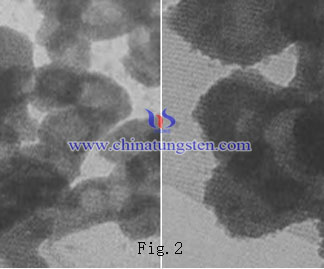
Figure 2 is a molybdenum disulfide hollow nanospheres TEM image in different magnifications. Obviously, some balloons burst due to external impact, hollow sphere particle diameter is 300 ~ 100nm, wall thickness is about 10nm. Different rate of precipitation and ion concentration distribution determind the shell thickness of the core-shell structure.