Electrochemical Deposition
Introduction
Electrochemical deposition method means that under a certain electrolyte and operating conditions, with the help of the electric field, it can electrolyze metal or alloy, compound precipitation solution, non-aqueous solution or molten salt, usually accompanied by electronic gains and losses. This procedure exists difficulty level, properties and morphology of the deposited metal are influenced by the electrolyte composition, pH value, temperature, current density and other factors.
Another important application of electrochemical deposition is the electrophoretic coating, under the condition of direct current, when the resin bead of electric charge reaches the counter electrode, through discharge or energized, separate out the precipitate which is insoluble in water and attached to the surface of the workpiece which is going to be coated.
The reaction should be first reacted in the high density position of electric fluxline, such as edge corners and the tip of the material which is to be coated, after the depositing, material to be coated will have a degree of insulation, electrodeposit would move toward the low density position of electric fluxline, until surface is completely well-distributed.
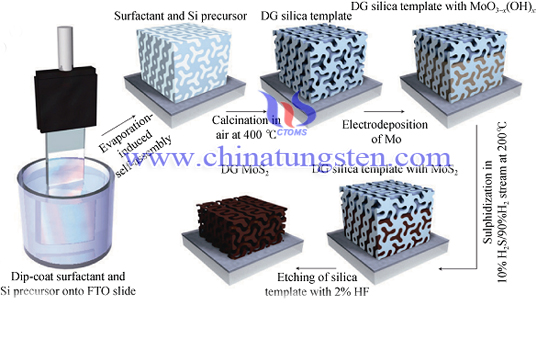
Molybdenum disulfide made by this method is an oxidation reduction reactions of aqueous solution spontaneous, anode and cathode is mounted at both ends of the device, form the electric field in the electrolyte, so that the chemical reaction can occur in the process of electrode. Firstly, MoO2 nanowires would be made from surface of HOPG by electrodeposition, and then it would convert into MoS2 at 800 ~ 900 ℃ and H2S atmosphere. Obtained by this method of MoS2 is nano-2H-type crystal structure with a thickness of 2 ~ 30 nm. Double helix twenty-four face MoS2 made by electrodeposition method and template, thickness of MoS2 web is about 4 nm, a width of 3 nm, the distance between the holes is 7 nm.

