Precursor Decomposition
Introduction
Precursor decomposition method is also known as lift-off method, which can produce molybdenum disulfide by thermal decomposition through tetrathiomolybdate directly without any solid or liquid or a sulfur-containing compound.
(NH4) 2MoS4 = MoS3 + 2NH3 + H2S and then decompose at high temperature MoS3: MoS3 = MoS2 + 1 / 8S8
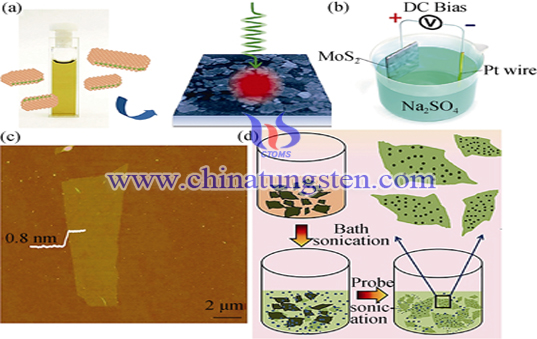
Crystallinity of nano MoS2 made by precursor decomposition has a high quality without any impurities, and the operation is simple, which is applicable to the preparation of a single device. But there are also some disadvantages, such as it is difficult to repeat, and it cannot mass production and so on. The reaction material is placed in an inert gas (Ar) environment for 2 days, to obtain the release intercalation LixMoS2, then clean the sample to neutral status successfully prepared layered MoS2 (a), after annealing at 300 ℃,the phase-Metal of release material would become phaseof semiconductor.
Through electrochemical stripping method, users can successfully prepared a large area of MoS2 nanosheets. Successfully prepared monolayer MoS2 by mechanical peeling method whose thickness is about 0.8 nm (c). By liquid stripping, dotted layered nanostructures MoS2 of MoS2 quantum dots can be successfully prepared, and MoS2 quantum dot size is about 2 nm, MoS2 sheet lateral dimension is approximately 1 μ m (d).
Such production method is simple, but the decomposition of molybdenum disulfide is too sensitive, as long as the reaction parameters (heating rate, final temperature, gas type, Kia and air velocity) slightly changes, there will be great changes on the surface of molybdenum disulfide. This method needs to prepare precursors at first, which played a key role in MoS2 production.

