Surfactant
Introduction
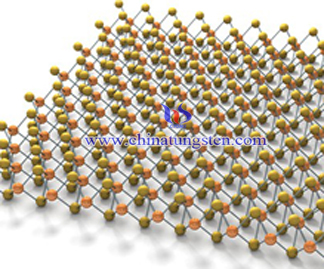
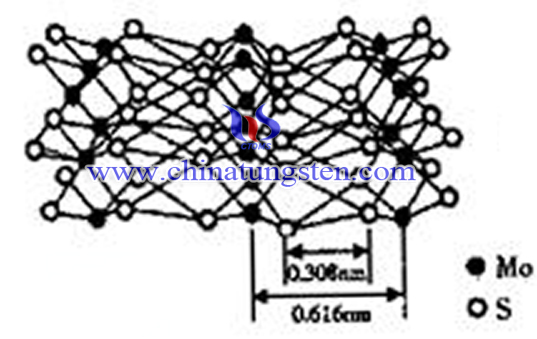
Surfactant means a kind of material which can make the interface state of solution system change significantly by adding a small amount substances. Surfactant belongs to hydrothermal method and solution method, but due to special regulation, it is classified into another type. This method is based on the hydrothermal method and solution method, adding one or more surfactants to control the particle size and pattern, and to improve structural performance. Overall performance of molybdenum disulfide prepared by this method is better.
Add cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) in MoS2 as a surfactant, it can produce high activity catalysta whose specificial area is up to 210m2 / g single layer of molybdenum disulfide. Structure is very stable in H2S / H2 mixed gas after maintaining 400 ~ 500 ℃ vulcanization, and it would not contain any other intermediate phase. Such catalyst is five times higher than commercial catalysts.
Surfactant method has a great advantage in improving the product appearance and structural properties, it is suitable to large-scale production. However, crystalline state of MoS2 made by this method is poor, the risk lies in its unique morphology and structure may occur structure collapse and disappear in the follow-up heat treatment, affecting the effectiveness of end-use.