Molybdenum Disulfide Nanoparticle Processes - Sodium Sulfide
Introduction
12g of sodium molybdate crystals (NaMoO4, AR) and 60g crystal sodium sulfide (Na2S, AR) are dissolved in 250ml of distilled water. They are poured into a 80ml ethanol catalyst beaker, to be stired mixed. Next, 3.6mol / l sulfuric acid is poured into 150ml beaker, and to be stired. Reaction is finished immediate, and release hydrogen sulfide gas. After completion of the reaction, obtain brown paste MoS3 precipitate. The precipitate is washed repeatedly with distilled water until the filtrate is neutral. The MoS3 precipitate is placed in dry in loft drier at 60℃ for 8h, it would be pulverized into small particles with a mortar. And then it is put into a tubular furnace at hydrogen atmosphere at 400 - 800℃ for 20min, end gas is absorbed by lye, and finally get silver MoS2 particles.
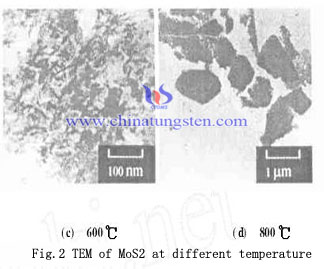
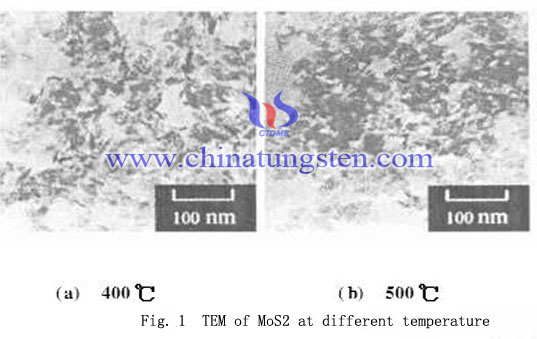
Crystalline state of MoS2 made at 400, 500 and 600℃ is not good, with varying degrees of distortion of the crystal lattice. The peak at 800 ℃ of MoS2 is significantly lower than the other three sharp peak temperature obtained. Figure 1 shows the MoS2 particle size generated in the 400, 500 and 600℃ are small and uniform particle size distribution, but there is a small amount of agglomeration. MoS2 is good hydrodesulfurization catalyst, during the reaction process if there are a amount of MoS3 is reducted with hydrogen and became MoS2, which would accelerate the reaction, crystal nucleus have no time to grow, resulting the imperfect crystalline state with varying degrees of distortion. And the crystal grain size is small, about 20 ~ 30nm (Fig. 1a, b, c). In 800℃, due to high temperatures promote the development and growth of nuclei, the crystalline state of MoS2 and elemental molybdenum obtained by calcining well without lattice distortion, and the resultant has larger particle size.