CVD
Introduction
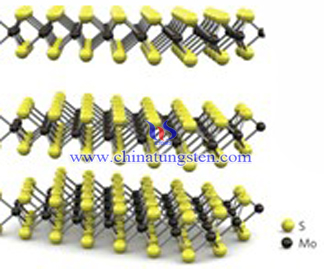
CVD method is to decompose the Mo and solid precursor of S at a high temperature, releasing Mo and S atoms would deposite on the substrate, and gradually grow into a film of MoS2.
Use sulfur powder as sulfur source, molybdenum trioxide powder provides Mo, a single atomic layer MoS2 film can be made by CVD method. Wherein the graphene oxide (rGO), PTAS or 3,4,9,10 perylene dianhydride (PTCAD) solution prior dropping on SiO2 / Si substrate are used as the seed, MoS2 first to grow around it, and to promote MoS2 forming a thin film.
Mo may also be provided by a Mo metal layer. Gatensby sputtered a certain thickness (0.5-20nm) of Mo metal layer as a source on the SiO2 / Si substrate and placed in dual-zone quartz tube furnace. In another heated zone, sulfur powder provide sulfur gas to the reaction zone for vulcanization. Mo metal layer sputtered on the substrate can also be used to control the shape of the film and the growth regional MoS2 film. Thickness of the film of the metal layer can be well adjusted by controlling the thickness of the metal and obtain the thinnest MoS2 (0.5nm) which is pure.
CVD method has Characteristics of an adjustable size, number of layers can be controlled, high quality of molybdenum disulfide nanosheets, which have excellent electrical properties. What's more, CVD can obtain a large area MoS2 film.